Cluster Installation: Difference between revisions
Spothineni (talk | contribs) |
Spothineni (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== XDS Cluster setup == | == XDS Cluster setup == | ||
In order to setup XDS in cluster mode, forkcolspot and forkintegrate scripts need to be changed to access the gridengine environment and send jobs to different machines. Example scripts are below, need to be changed according to the environment. | In order to setup XDS in cluster mode, ''forkcolspot'' and ''forkintegrate'' scripts need to be changed to access the gridengine environment and send jobs to different machines. Example scripts are below, need to be changed according to the environment. | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 157: | Line 157: | ||
echo $image1 $nitask $itask $nbatask | mintegrate_par | echo $image1 $nitask $itask $nbatask | mintegrate_par | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
== Grid Engine Installation == | == Grid Engine Installation == | ||
Revision as of 19:05, 8 June 2015
XDS can be run in cluster mode using any command line job scheduling software such as Grid Engine, Condor, Torque/PBS, LSF, SLURM etc. We implemented Grid Engine. It is a distributed resource management system which monitors the CPU and memory usage of the available computing resources and schedules the job to the least used computer. Grid Engine was chosen due to its high scalability, cost effectiveness, ease of maintenance and high throughput. Grid Engine was developed by Sun Microsystems (Sun Grid Engine, SGE) and later acquired by Oracle and subsequently acquired by UNIVA. The latest versions became closed source, but the older ones are open source supplied with many Linux distributions including Redhat/CentOS 6.x. There is also open source Open Grid Scheduler [[1]], Son of Gridengine [[2]]
XDS Cluster setup
In order to setup XDS in cluster mode, forkcolspot and forkintegrate scripts need to be changed to access the gridengine environment and send jobs to different machines. Example scripts are below, need to be changed according to the environment.
#forkcolspot
ntask=$1 #total number of jobs
maxcpu=$2 #maximum number of processors used by each job
#maxcpu=1: use 'mcolspot' (single processor)
#maxcpu>1: use 'mcolspot_par' (openmp version)
pids="" #list of background process ID's
itask=1
echo "MAX CPU $maxcpu $image1"
#Sudhir check for gridengine submit host
submitnodes=`qconf -sh 2> /dev/null`
thishost=`hostname`
isgrid=0
for node in $submitnodes ; do
if [ "$node" == "$thishost" ]
then
isgrid=1
echo "Grid Engine environment detected"
fi
done
while test $itask -le $ntask
do
if [ $maxcpu -gt 1 ]
# then echo "$itask" | mcolspot_par &
# else echo "$itask" | mcolspot &
then
if [ $isgrid -eq 1 ]
then
qsub -sync y -V -l h_rt=0:20:00 -cwd \
forkcolspot_job \
$itask &
#else echo "$itask" | qrsh -V -cwd "mcolspot" &
else echo "$itask" | mcolspot_par &
fi
else echo "$itask" | mcolspot &
fi
pids="$pids $!" #append id of the background process just started
itask=`expr $itask + 1`
done
trap "kill -15 $pids" 2 15 # 2:Control-C; 15:kill
wait #wait for all background processes issued by this shell
rm -f mcolspot.tmp #this temporary file was generated by xds
rm -rf fork*job*
#forkcolspot_job #!/bin/csh echo $1 set itask=$1 echo $itask | mcolspot_par
#forkintegate
fframe=$1 #id number of the first image
ni=$2 #number of images in the data set
ntask=$3 #total number of jobs
niba0=$4 #minimum number of images in a batch
maxcpu=$5 #maximum number of processors used by each job
#maxcpu=1: use 'mintegrate' (single processor)
#maxcpu>1: use 'mintegrate_par' (openmp version)
minitask=$(($ni / $ntask)) #minimum number of images in a job
mtask=$(($ni % $ntask)) #number of jobs with minitask+1 images
pids="" #list of background process ID's
nba=0
litask=0
itask=1
#Sudhir check for gridengine submit host
submitnodes=`qconf -sh 2> /dev/null`
thishost=`hostname`
isgrid=0
for node in $submitnodes ; do
if [ "$node" == "$thishost" ]
then
isgrid=1
echo "Grid Engine environment detected"
fi
done
while test $itask -le $ntask
do
if [ $itask -gt $mtask ]
then nitask=$minitask
else nitask=$(($minitask + 1))
fi
fitask=`expr $litask + 1`
litask=`expr $litask + $nitask`
if [ $nitask -lt $niba0 ]
then n=$nitask
else n=$niba0
fi
if [ $n -lt 1 ]
then n=1
fi
nbatask=$(($nitask / $n))
nba=`expr $nba + $nbatask`
image1=$(($fframe + $fitask - 1)) #id number of the first image
if [ $maxcpu -gt 1 ]
then
if [ $isgrid -eq 1 ]
then
qsub -sync y -V -l h_rt=0:20:00 -cwd \
forkintegrate_job \
$image1 $nitask $itask $nbatask &
#else echo "$image1 $nitask $itask $nbatask" | qrsh -V -cwd "mintegrate" &
else echo "$image1 $nitask $itask $nbatask" | mintegrate_par &
fi
else echo "$image1 $nitask $itask $nbatask" | mintegrate &
fi
pids="$pids $!" #append id of the background process just started
itask=`expr $itask + 1`
done
trap "kill -15 $pids" 2 15 # 2:Control-C; 15:kill
wait #wait for all background processes issued by this shell
rm -f mintegrate.tmp #this temporary file was generated by mintegrate
rm -rf fork*job*
#forkintegrate_job
#!/bin/csh
set image1=$1
set nitask=$2
set itask=$3
set nbatask=$4
set host=`uname -a | awk '{print $2}'`
echo $image1 $nitask $itask $nbatask $host >> jobs.log
echo $image1 $nitask $itask $nbatask | mintegrate_par
Grid Engine Installation
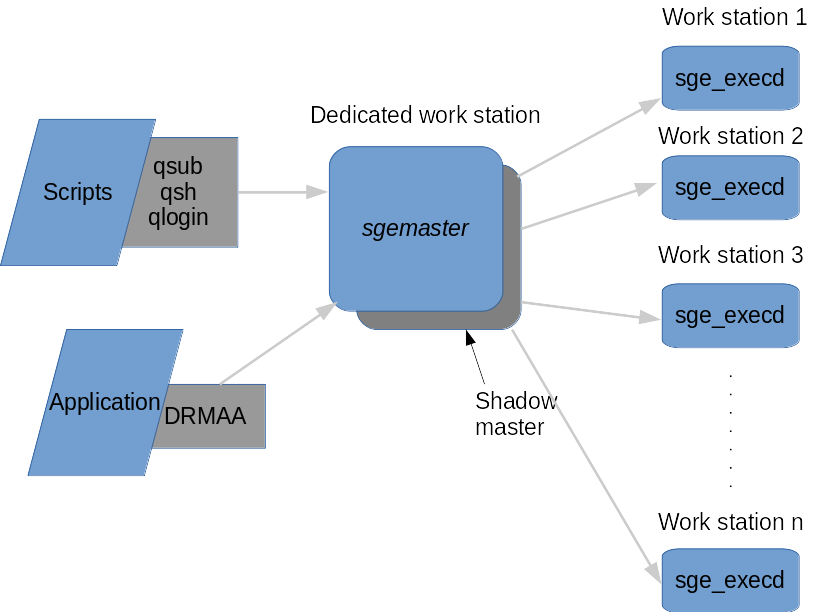
Grid Engine consists of a master node daemon named sgemaster which schedules jobs to execution nodes. On each execution node a daemon named sge_execd runs a job and sends a completion signal back to sgemaster. Jobs are submitted to sgemaster using command such as qsub or using DRMAA C, JAVA or IDL bindings from any applications want to run XDS.
Redhas/CentOS Linux distribution comes with rpms for installing Grid Engine. One need to have administrative privileges to install. Install gridengine rpms on all the nodes using following command, Default shell for Grid Engine is /bin/csh. It is assumed the all the workstations involved access the storage where the data is stored and authentication is done through protocols like LDAP.
root@sudhir:/home/spothineni 1> yum install gridengine gridengine-qmaster gridengine-execd gridengine-qmon root@sudhir:/home/spothineni 2> rpm -qa | grep gridengine gridengine-qmaster-6.2u5-10.el6.4.x86_64 gridengine-qmon-6.2u5-10.el6.4.x86_64 gridengine-execd-6.2u5-10.el6.4.x86_64 gridengine-6.2u5-10.el6.4.x86_64
By default gridengine installation directory /usr/share/gridengine, contents shown below.
root@sudhir:/home/spothineni 3> cd /usr/share/gridengine root@sudhir:/home/spothineni 4> ls bin default hadoop install_execd lib my_configuration.conf qmon utilbin ckpt doc inst_sge install_qmaster mpi pvm util
On bl1upper which qmaster node install using install_qmaster
root@bl1upper:/usr/share/gridengine 5>./install_qmaster
Most of the answers are yes/no or typing enter. Following things need to be decided before installation
- Admin user is root
- Following important environment variables are written to /usr/share/gridengine/default/common/settings.csh which should be in the $PATH.
- $SGE_ROOT=/usr/share/gridengine
- $SGE_QMASTER_PORT=6444
- $SGE_EXECD_PORT=6445
- $SGE_CELL=default
- JMX MBean server not used
- Spooling method used is classic
- There is an option to give administrative email which is very useful, when ever there is any problem gridengine will send error messages to email.
- Ready with a file contains admin and submit hosts or you can manually enter all the hosts separated by space, use full DNS names of hosts.
- In this installation shadow host is not used.
- After the shadow host step make sure allhosts group and all.q are created otherwise installation sge_execd will have problems.
- Scheduler Tuning selected as 'Max', it has disadvantage, gridengine immediately schedules with out assuming the load, this will cause successive job submissions will go to same host until all the slots are filled for that machine. Selecting 'Normal' will assume the load but there is overhead of few sec. extra time for job scheduling.
After finishing the installation the configuration files are automatically written to the directory /usr/share/gridengine/default since the cell name selected is 'default'. This directory can be choosen as a shared directory over NFS. Otherwise copy this directory to every host used int the cluster.
On execution node install execution daemon using following command
root@bl1ws1:/usr/share/gridengine 5>./install_execd
the input is almost typing return if you already copied the 'default' directory to this node.
Restarting Grid Engine
When grid engine installed first time /etc/init.d/sgemaster and /etc/init.d/sge_execd services are automatically installed. If you want to restart sgemaster make sure all the sge_execd deamons are stoped. You can do this by following commands
service sge_execd stop service sgemaster stop
for starting
service sge_execd start service sgemaster start
When ever work stations need to be restarted make sure sgemaster work station started first. To keep the services restarted automatically during the startup make sure chkconfig is on.
chkconfig sgemaster on chkconfig sge_execd on
Son of Gridengine
rpms available in this link
http://arc.liv.ac.uk/downloads/SGE/releases/8.1.8/
by defualt these rpms install in single directory /opt/sge instead of scattering (by default) files to /usr/bin, /usr/share/gridengine, /usr/spool/gridengine
Default shell for Son of Gridengine is /bin/sh which is /bin/bash