ILIAS/Instructions/Question types
1. Descriptive question types
1.1 Automatically evaluated questions:
| Question Type | Description | Special Features |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple Choice Question (Single Answer) | A question with multiple answer options (texts or images), of which only one is correct. Consequently, either all points or 0 points can be achieved.(Example) | |
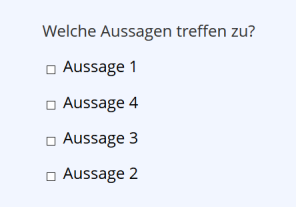
| Multiple Choice Question (Multiple Answers) | A question with multiple answer options (texts or images), where one or more may be correct. Negative points should be assigned so that giving wrong answers has an impact on the evaluation.(Example)
If this functionality is not sufficient for your needs and you prefer to have three options: 1.) to mark an answer considered correct as correct (and receive points or negative points as appropriate) 2.) to mark an answer considered incorrect as incorrect (and receive points or negative points as appropriate) 3.) not to mark either answer as correct or incorrect when unsure (and receive neither points nor negative points) - you can use the cloze text question (selection gap option) for this. (Example) |
|
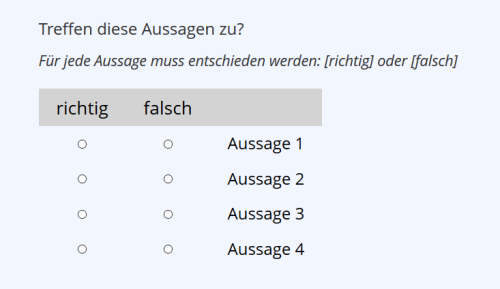
| Multiple Choice Question (Kprim Answers) | A question or incomplete statement with four answer or completion alternatives, each of which must be judged as correct or incorrect. Custom terms can be entered instead of the default terms “correct” and “incorrect”. Two evaluation options are available:A) If all four judgments are correct, the question is rated as correct with the desired score. Otherwise, you get 0 points.B) Activating the half-point evaluation means that three correct judgments receive half the points. Less than three correct judgments can only be scored with 0 points in both options.(Example) | |
| Matching Question | Various terms, definitions, or images must be matched by dragging and dropping them together. To reduce the chance of random hits, additional unmatched elements can be included.(Example) | not suitable for touchscreens
|
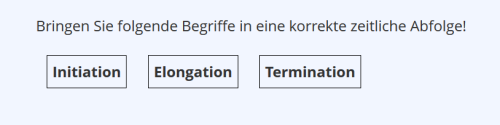
| Ordering Question | Different terms or images need to be arranged in the correct (e.g., hierarchical or chronological) order or cause-and-effect relationship by dragging and dropping.(Example) | not suitable for touchscreens
|
| Error Text | In an error text, all words or groups of words that are incorrect or make no sense must be marked by clicking.(Example) | |
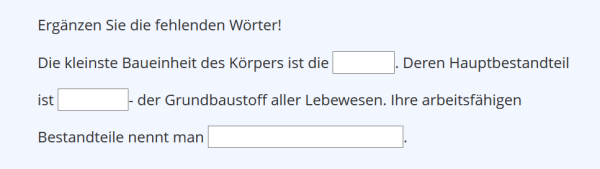
| Cloze Question | An incomplete text needs to be completed:- Text gap, where the correct supplementation must be entered in the input field- Selection gap, where the correct answer must be marked from multiple options- Numerical gap (for calculation or estimation tasks), where a calculated or estimated value must be entered (a number or range can be specified).(Example) | |
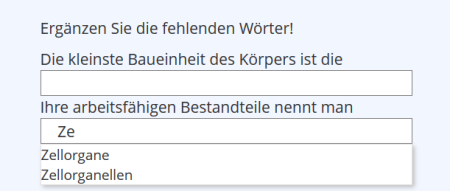
| Long Menu | A combination of cloze text and single choice: the gap in the sentence must be completed, but answer alternatives are offered as autocomplete after a specified number of correctly entered characters. The question allows for testing existing knowledge while avoiding spelling mistakes – especially with long terms – through autocomplete.(Example) | |
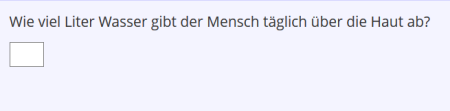
| Numeric Question | A numerical value must be entered (a specific number or range can be specified).(Example) | |
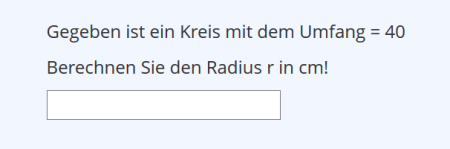
| Formula Question | Calculation tasks must be solved. The task and solution path (the correct formula) are defined, but ILIAS randomly provides the values to use for the calculation: Participants receive different, random values and thus different results (value range and divisibility can be specified).(Example) | |
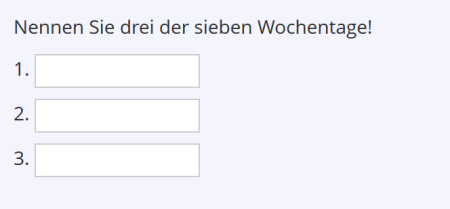
| Text Subset Question | In response to a question, one or more terms must be named. When creating the question, it is defined which terms are correct and how many terms must be named.(Example) | |
| Image Map Question | The correct answer must be given by clicking on a predefined interactive area of an image or graphic.(Example) |
1.2 Manually evaluated questions:
| Question Type | Description | Special Features | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Essay Question | An open-ended question that is answered with a text entry. Possible options are:- specifying a maximum character count- defining keywords that permit point allocation if mentioned (manual review is indispensable).(Example) | ||
| Long Text Essay Task | This question type is suitable for all tasks that require participants to write longer texts. This question type is implemented in a standalone object (not in the ILIAS test object) and is therefore primarily suitable for examinations solely focused on text writing. The long text task is significantly more comfortable for both the participants and the graders than the standard free text question. This question type is very new and is developing rapidly; we are happy to inform you about the current possibilities in a consultation session.(more info) | ||
| File Upload Question | A solution created in another program (e.g., sketches, calculations, presentations, computer programs) is submitted in response to an open question.(Example) | not suitable for Chromebook and Bring Your Own Device exams | |
| Paint Question | Freehand drawings can be created, e.g., on a specific background image. The drawing is done (with few exceptions) freehand with the mouse or, if available, a stylus. If no stylus is available, the requirement should not be too complex.(Example) | ||
| JSME Question | The graphical representation of structural formulas of simple and complex molecular compounds can be queried. The question or task is answered using the integrated JSME Molecule Editor. When creating the question, a model answer can be created, also using the integrated JSME Molecule Editor.(Example) |
2. Beispiele und zusätzliche Infos zu den Fragetypen
Multiple Choice Question (Single Answer)
| Beispiel: |
|---|

|
Multiple Choice Question (Multiple Answers)
| Beispiel: |
|---|
|
Multiple Choice Question (Kprim Answers)
| Beispiel: |
|---|
|
Matching Question
| Beispiel: |
|---|

|
Ordering Question
| Beispiel: Horizontale Anordnungsfrage: |
|---|
|
| Beispiel: Vertikale Anordnungsfrage: |
|---|

|
Error Text
| Beispiel: |
|---|

|
Cloze Question
| Beispiel: |
|---|
|
Long Menu
| Beispiel: |
|---|
|
Numeric Question
| Beispiel: |
|---|
|
Formula Question
| Beispiel: |
|---|
|
Text Subset Question
| Beispiel: |
|---|
|
Image Map Question
| Beispiel: |
|---|
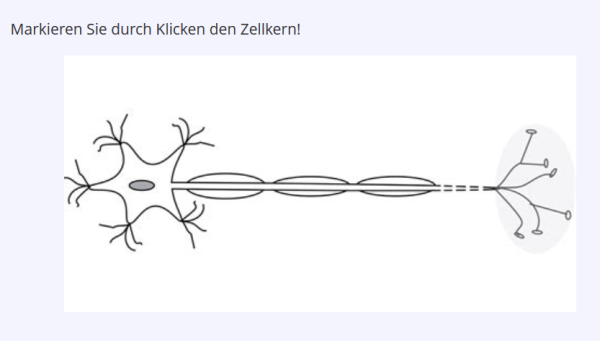
|
Essay Question
| Beispiel: |
|---|
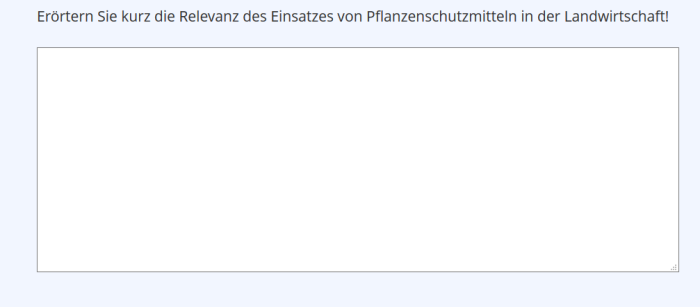
|
Long Text Essay Task
This question type is implemented in a separate object (and not in the ILIAS test object) and is therefore primarily suitable for exams that only include writing texts. The long text task is significantly more comfortable for both participants and correctors than the normal free text question.
Some of the most important features of the long text task for participants:
- Texts can be structured with subheadings and formatted in various ways (can be disabled upon request).
- The interface is comparatively user-friendly. It allows for flexible switching between different views without loading time: one's own answer, the task or tasks, additionally provided PDF material, or a view with both side by side.
- Additional materials such as PDFs or web links can be included.
- The entered text is cached in the browser but constantly synchronized with ILIAS, so nothing is lost in case of connection interruptions or hardware problems. (Often, the capabilities of the free text question are already sufficient here. However, the long text task synchronizes much more frequently and reliably.)
- Besides the actual answer, notepads are available for making notes. Copy-and-paste between the answer and the notepads is, of course, possible. The content of the notepads remains confidential and is irretrievably deleted upon submitting the answer. (Notepads can be disabled upon request.)
Useful features for correctors:
- Highlights and annotations can be added directly to the text via a convenient interface.
- Points can also be awarded in these annotations. The sum of these points is displayed, but the total score can also be awarded independently of them (e.g., if you don't want to use this feature).
- Of course, an overall impression can be formulated in the running text.
- A correction workflow with multiple correctors can be well organized.
- During the correction, the participant's name is not displayed, and the correction is anonymized. Only the course administrator can find out who a specific answer is from – but this is not automatically displayed during correction.
- In case students feel that parts of their answer have "disappeared" or have been "devoured," it is possible to trace the individual editing steps while writing. For example, it can be determined when large sections of one's own essay were accidentally deleted in the hustle and bustle of an exam. (Of course, whether to consider these sections as a courtesy in grading is at the discretion of the lecturers.)
This question type is still quite new and developing rapidly; we are happy to inform you about the currently available options in a consultation session.
File Upload Question
| Beispiel: |
|---|
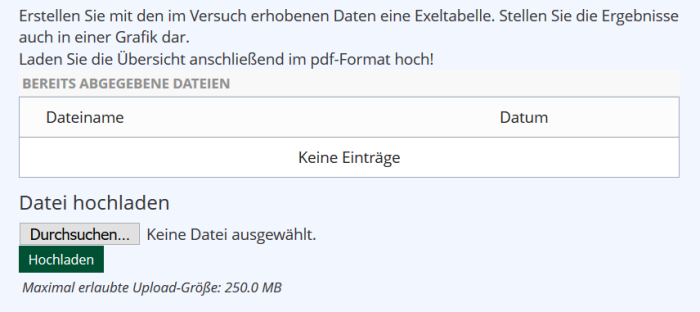
|
Paint Question
| Beispiel: |
|---|

|
JSME-Question
| Beispiel: |
|---|
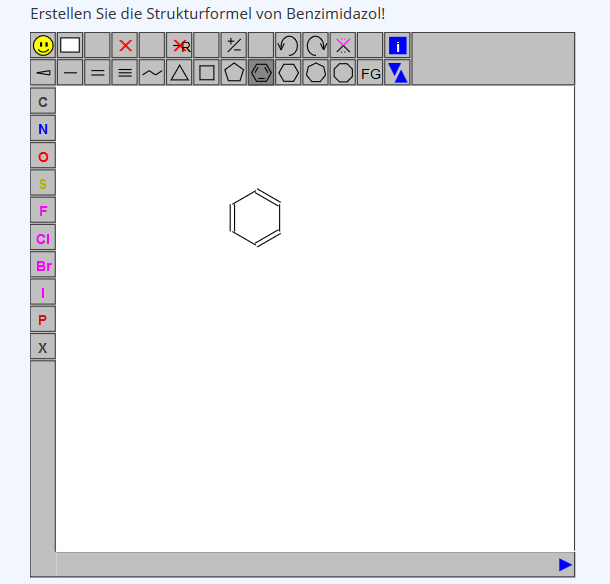
|
Links
- Many information and screenshots of this page are taken from the Overview of Question Types of the E-Learning Knowledge Portal for Instructors (Wiki) of Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg.